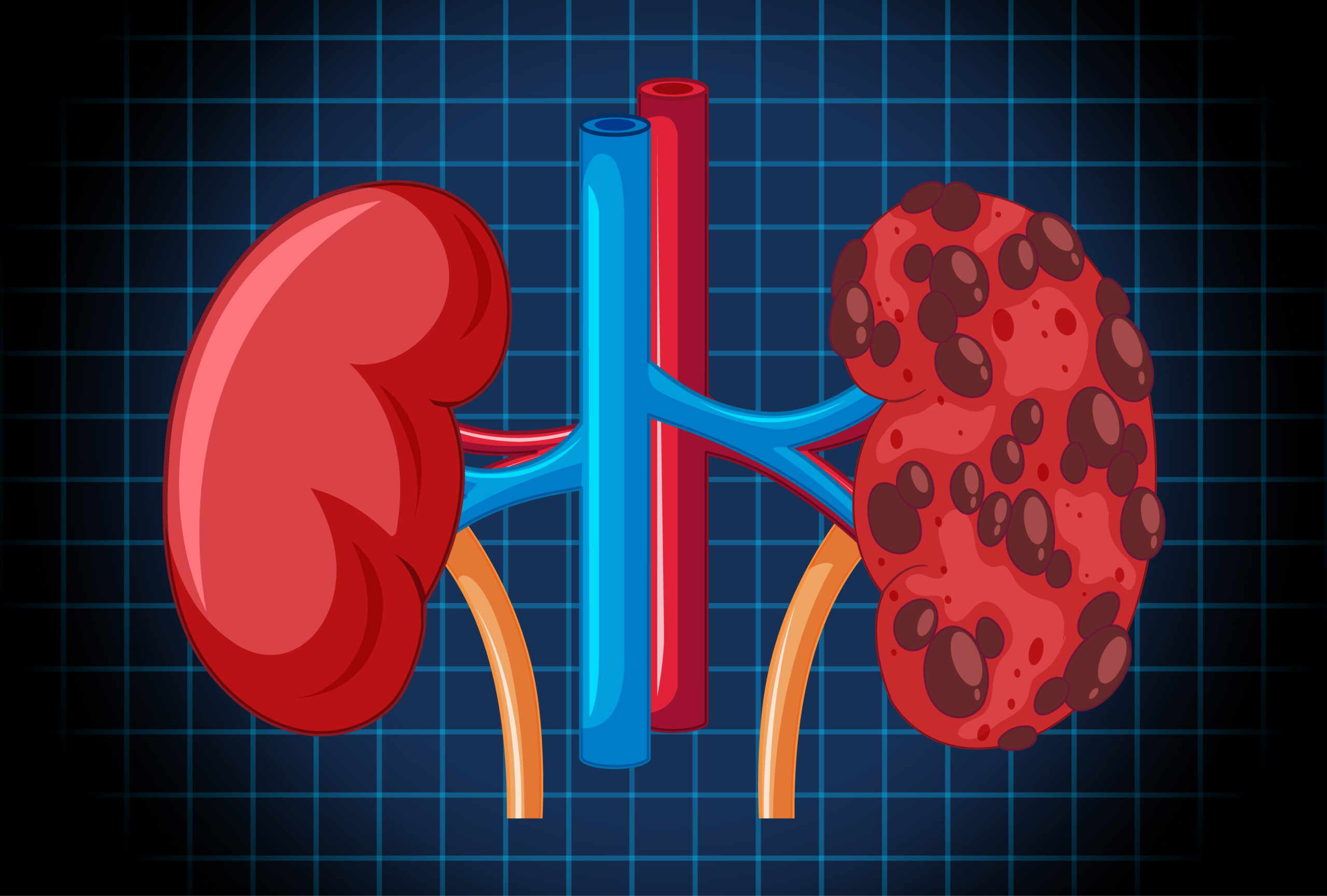
What Is Polycystic Kidney Disease?
Polycystic Kidney Disease (PKD) is a genetic condition. It causes many fluid-filled sacs, called cysts, to grow in the kidneys. Over time, these cysts can make the kidneys larger and less able to work well. Because PKD can run in families, knowing your risk is important. Early detection helps manage the disease and prevent serious problems.
Common Symptoms of PKD
PKD symptoms can be mild at first. However, they often get worse as the cysts grow. It is important to watch for signs early. Some people may not notice symptoms until the disease has advanced. Still, knowing what to look for can help with early diagnosis.
Why Early Diagnosis Matters
Early diagnosis of Polycystic Kidney Disease is very important. When PKD is found early, doctors can help slow its progress. For example, they can treat high blood pressure and prevent kidney damage. In addition, early care can help you avoid complications, such as kidney failure. Because PKD can affect other organs, early detection also helps manage related health issues.
Diagnostic Tests for PKD
Doctors use several tests to diagnose PKD. These tests help find kidney cysts and check how well your kidneys work. If you have a family history of PKD, your doctor may suggest testing even if you feel fine. Let’s look at the main ways PKD is diagnosed.
Imaging Tests (Ultrasound, CT, MRI)
Imaging tests are often the first step in diagnosing PKD. They help doctors see cysts in the kidneys. Each test has its own benefits.
Genetic Testing
Genetic testing looks for changes in the genes that cause PKD. This test is helpful if you have a family history but no clear symptoms. It can also confirm a diagnosis when imaging results are unclear. However, not everyone needs genetic testing. Your doctor will help you decide if it is right for you.
Blood and Urine Tests
Blood and urine tests check how well your kidneys are working. They do not show cysts, but they help doctors see if PKD is affecting kidney function. These tests can also find signs of infection or other problems.
What to Expect During Diagnosis
When you visit your doctor for PKD diagnosis, you will answer questions about your health and family history. Next, your doctor will do a physical exam. After that, you may have imaging tests, blood tests, or urine tests. Most tests are simple and do not cause pain. However, some people may feel nervous. Remember, your care team will explain each step and answer your questions.
Frequently Asked Questions About PKD Diagnosis
Prevention and Next Steps After Diagnosis
There is no way to prevent PKD if you have the genes for it. However, early diagnosis helps you manage the disease and protect your kidneys. After diagnosis, your doctor may suggest lifestyle changes, regular check-ups, and medicines to control blood pressure. In some cases, you may need treatment for infections or other problems. Staying informed and working with your care team can help you live a healthier life with PKD.
For more information, visit trusted sources like the National Kidney Foundation or the CDC.
Consult a nephrologist for personalized advice and early diagnosis of Polycystic Kidney Disease.